0ff9c33b:3ad45af8
posted
2 days ago
🥇ผลสลากกินแบ่งรัฐบาล งวด 16 พ.ย.67
🔰สมัครได้ที่ bit.ly/3Dm16iR
✅ครบจบที่เดียว มั่นคงปลอดภัย
⚽️ Lotto432 หวยออนไลน์
#ตรวจหวย #ถ่ายทอดสด #หวยออก
#หวยงวดนี้ #ผลหวย #หวย #สลากกินแบ่งรัฐบาล #หวยรัฐบาล #หวยรัฐบาลไทย
#รางวัลที่1 #เลขท้าย2ตัว
#siamstr #nostr #siamstrong
#bitcoin #fiat #usdt #sat #satoshi
#Lotto432 #หวย #หวยออนไลน์ #usdt
#อัตราจ่ายแพงที่สุด #เปิดไพ่รับเงินล้าน
#คาสิโน #ฟุตบอล #สล็อตแมชชีน #สล็อต
#lottery #Lotto #กีฬา #หวยรัฐบาล 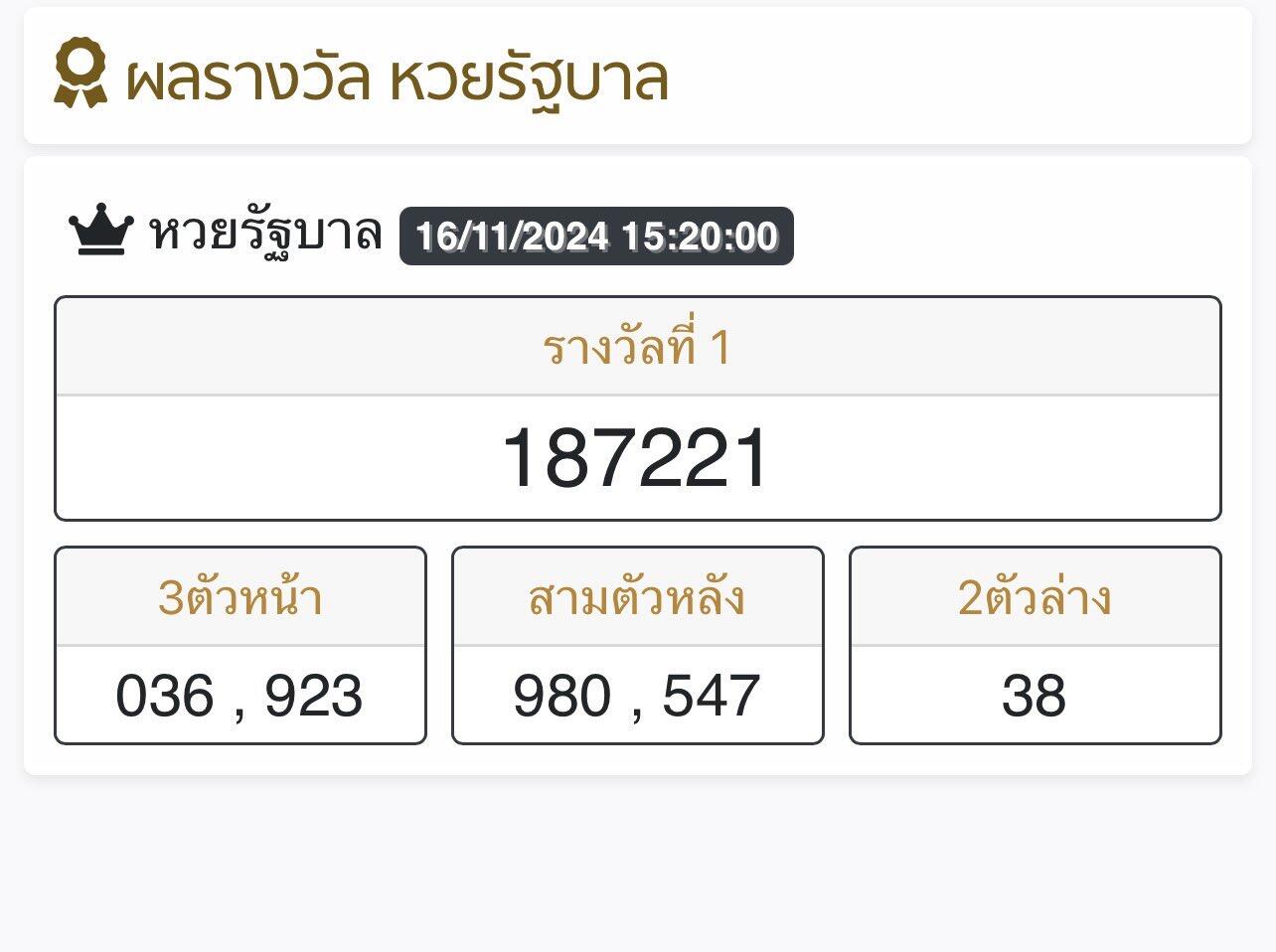

bharat
posted
2 days ago
Such a good point.
bharat
posted
2 days ago
Enjoy.
863f2c55:87fee183
posted
2 days ago
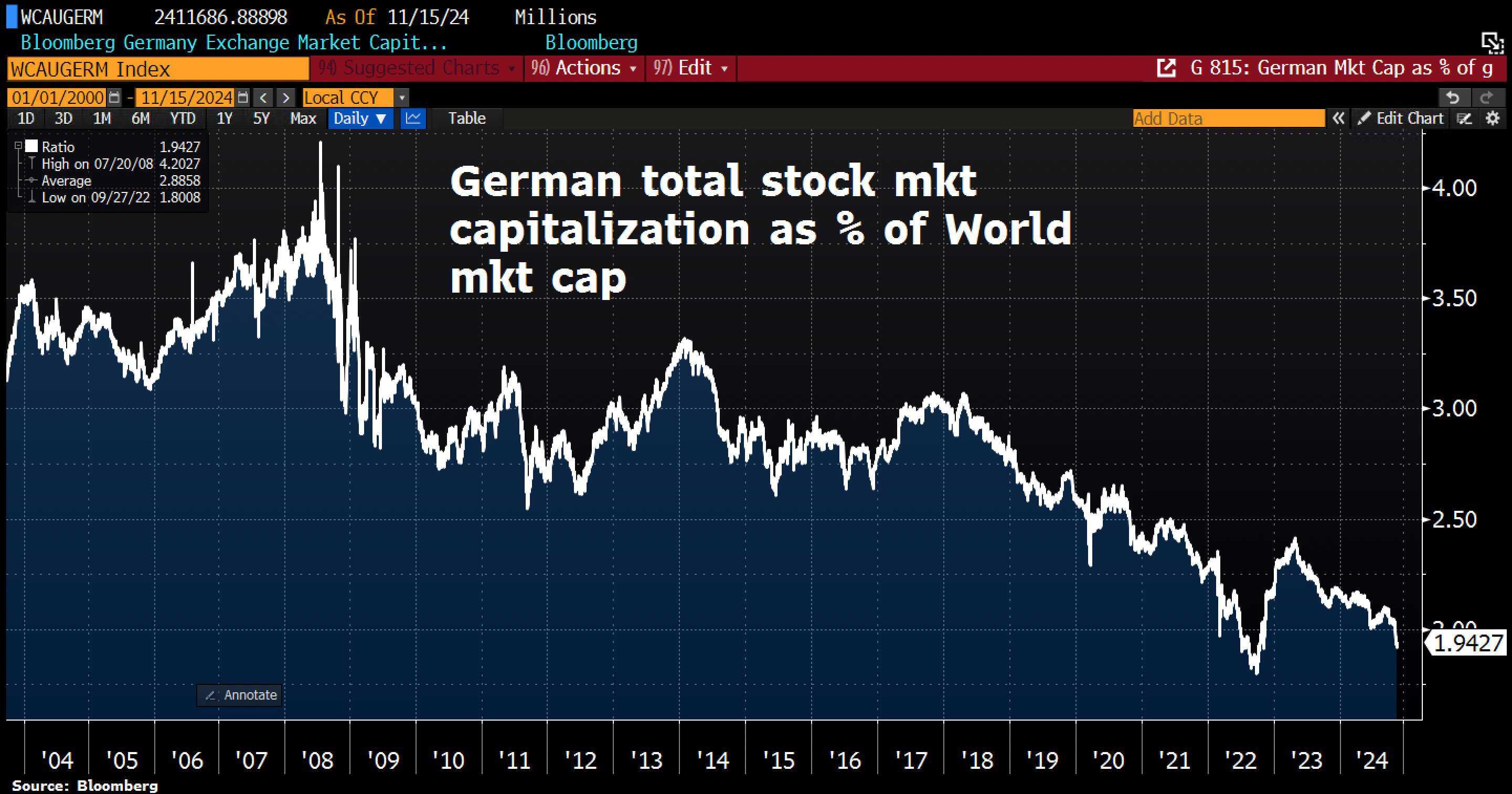
Germany: the melting of the geopolitical iceberg
The major financial crisis of 2008 and 2009, which turned into a massive sovereign debt crisis in the European Union, was merely roughly washed over in the familiar Keynesian pattern, with interest rate manipulation and cheap money, Mario Draghi: 'whatever it takes'. The price that the Germans in particular have to pay for never having returned to real money, to a free market economy, is the disappearance into no man's land in the geopolitical rankings, which is also documented by the relative capitalization of the stock market in Germany. It is possibly the biggest descent story of the current century.
#Germany #stock market #geopolitics #socialism #eu #bitcoin

5b5bb4c7:621ef377
posted
2 days ago
How About The Sun Docking To The Hillside?
This is #Cyprus 🇨🇾 #sunset #photography #photostr #picstr 

Cyph3rp9nk
posted
2 days ago
This proves that Nostr is the authentic decentralized platform.
Cyph3rp9nk
reposted
2 days ago
{"id":"b571bd38578780c0e4052a3ab4a7fced29853b236f0628ac02426ef0bed3c757","sig":"7e49c02220280af3483b674381cdd3a31808ed2cd051dbae3563dfa9b96efd2f8db24bd562621c88bcc3650ecfbd88850dfdc25a0ea1a9532fab285fd5faad35","kind":1,"tags":[],"pubkey":"1bc70a0148b3f316da33fe3c89f23e3e71ac4ff998027ec712b905cd24f6a411","content":"It’s so weird that whenever there are discussions about decentralized platforms I see bluesky mentioned every time but zero mention of nostr - like it doesn’t exist. \n\nSome bizarre universe or what","created_at":1731748436}
Karnage
posted
2 days ago
It’s so weird that whenever there are discussions about decentralized platforms I see bluesky mentioned every time but zero mention of nostr - like it doesn’t exist.
Some bizarre universe or what
Escitalopram Why?
posted
2 days ago
and therefore...most realistic
Escitalopram Why?
reposted
2 days ago
{"id":"01ee9ebe3e57f6445d12fddcdf0931e9e63e9143c99cc1da48df04f80062d9f1","pubkey":"6e75f7972397ca3295e0f4ca0fbc6eb9cc79be85bafdd56bd378220ca8eee74e","created_at":1731745909,"kind":1,"tags":[["client","noStrudel","31990:266815e0c9210dfa324c6cba3573b14bee49da4209a9456f9484e5106cd408a5:1686066542546"],["nonce","94","7"]],"content":"If you want to live on the edge place your coffee mug in front or next to the keyboard instead of behind it.","sig":"b7f0730a1c73567f0656608c9e40da040eca43b4362a9661a4c8ded17b1d7dd1715772328c91d44f14a54f26de58ba9f67d5c383d5ecf565f0f49f5d6456ca13"}
Escitalopram Why?
posted
2 days ago
you're black enough, sure
b6de0eec:f536a2f6
posted
2 days ago
Potrebbe tornare di moda l'incidentenauticio. cerchiamo di non esagerare però...
 Ho perso tutti i miei amici #normie in un incidente nautico.
- CraigyD
#quotes #sovereign #citazioni #freedom #pensieri #parole #libertà #wisdom #anima #filosofia #poesia #Bitcoin #Nostr
Ho perso tutti i miei amici #normie in un incidente nautico.
- CraigyD
#quotes #sovereign #citazioni #freedom #pensieri #parole #libertà #wisdom #anima #filosofia #poesia #Bitcoin #Nostr
 Ho perso tutti i miei amici #normie in un incidente nautico.
- CraigyD
#quotes #sovereign #citazioni #freedom #pensieri #parole #libertà #wisdom #anima #filosofia #poesia #Bitcoin #Nostr
Ho perso tutti i miei amici #normie in un incidente nautico.
- CraigyD
#quotes #sovereign #citazioni #freedom #pensieri #parole #libertà #wisdom #anima #filosofia #poesia #Bitcoin #Nostr
0f389bba:9b3f148f
posted
2 days ago
🌊 SURF 'N TURF 🏝️
-THE ISLAND LIFE-
https://image.nostr.build/8daa0858c6015b223d471b3477401780cac46a4ac985fa3fef9ade825f98b98c.jpg
On this day in 1971, the Don McLean’s second LP “American Pie” debuted on the US Billboard 200 Albums Chart at #164 (November 13)
The folk rock album containing the classic chart-topping singles "American Pie" and "Vincent" eventually reached #1 on the Billboard 200, and also topped the charts in Australia and Canada, and went to #2 in the UK.
McLean has said that for this LP he was influenced by the Beatles' Sgt Pepper album.
Interestingly, producer Ed Freeman decided to use accomplished musicians who were not "studio musicians who could act like a metronome" because he wanted to capture the feel of a "band that was really cooking”.
Click on the link below to watch Don McLean do it live:
https://youtu.be/RciM7P9K3FA
Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
₿$₱
posted
2 days ago
$91,424.87 / #bitcoin
≅ ₱5,370,685.71
🟢 0.32% ≅ ₱17,132.29
Cyph3rp9nk
reposted
2 days ago
{"id":"119fba69ae3d938f763ebb698630782cd366bd4a0401c5d303491e9dd6fc2e4c","pubkey":"6389be6491e7b693e9f368ece88fcd145f07c068d2c1bbae4247b9b5ef439d32","created_at":1731743317,"kind":1,"tags":[],"content":"The ETH/BTC ratio is the best way to look at the relationship between the two.\n\nSince June 2017 the opportunity cost of holding ETH has done nothing but rise. That's 7 years of loss against the value of bitcoin in purchasing power and for the last 15 weeks that ratio has been falling like a stone.\n\nThe two darker blue lines are the long-term downward trough while the light blue line is ETH tilting its nose down and aiming firmly for the ground.\n\nWe have warned and warned and warned. We've been laughed at, made fun of, and called \"Maximalists\". We were right in 2017, we are right now, and will be right going forward.\n\nhttps://m.primal.net/MXjE.png \nhttps://m.primal.net/MXjJ.png ","sig":"d050de9151642715878d72f738acd480d87c95acf00705097d60a3e4beb79d70958a73e3e381499d2f2fc44bc8cc3f8bdba91bf2b3a6ccc1f321eb53dbf486ad"}
0f389bba:9b3f148f
posted
2 days ago
🌊 SURF 'N TURF 🏝️
-THE ISLAND LIFE-
Hans Zimmer
Moog modular with Roland System 700 cabinets.
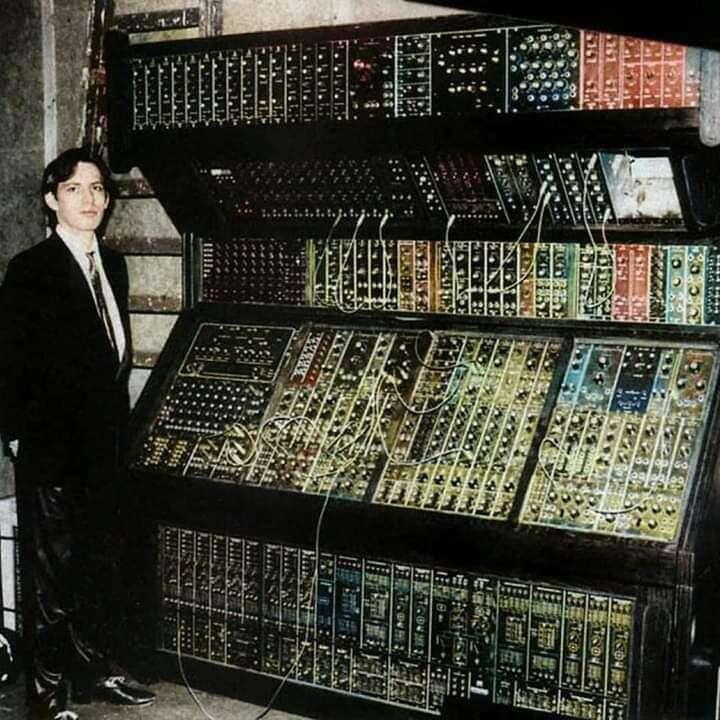 His works are notable for integrating electronic music sounds with traditional orchestral arrangements. Since the 1980s, Zimmer has composed music for over 150 films.
He has won two Academy Awards for Best Original Score for The Lion King (1994), and for Dune (2021). His works include Gladiator, The Last Samurai, the Pirates of the Caribbean series, The Dark Knight trilogy, Inception, Man of Steel, Interstellar, Dunkirk, No Time to Die, and the Dune series.
Zimmer spent the early part of his career in the United Kingdom before moving to the United States. He is the head of the film music division at DreamWorks Pictures and DreamWorks Animation studios and works with other composers through the company that he founded, Remote Control Productions, formerly known as Media Ventures.
His studio in Santa Monica, California, has an extensive range of computer equipment and keyboards, allowing demo versions of film scores to be created quickly.
Zimmer has collaborated on multiple projects with directors including Christopher Nolan, Ridley Scott, Ron Howard, Gore Verbinski, Michael Bay, Guy Ritchie, and Denis Villeneuve.
Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
His works are notable for integrating electronic music sounds with traditional orchestral arrangements. Since the 1980s, Zimmer has composed music for over 150 films.
He has won two Academy Awards for Best Original Score for The Lion King (1994), and for Dune (2021). His works include Gladiator, The Last Samurai, the Pirates of the Caribbean series, The Dark Knight trilogy, Inception, Man of Steel, Interstellar, Dunkirk, No Time to Die, and the Dune series.
Zimmer spent the early part of his career in the United Kingdom before moving to the United States. He is the head of the film music division at DreamWorks Pictures and DreamWorks Animation studios and works with other composers through the company that he founded, Remote Control Productions, formerly known as Media Ventures.
His studio in Santa Monica, California, has an extensive range of computer equipment and keyboards, allowing demo versions of film scores to be created quickly.
Zimmer has collaborated on multiple projects with directors including Christopher Nolan, Ridley Scott, Ron Howard, Gore Verbinski, Michael Bay, Guy Ritchie, and Denis Villeneuve.
Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
 His works are notable for integrating electronic music sounds with traditional orchestral arrangements. Since the 1980s, Zimmer has composed music for over 150 films.
He has won two Academy Awards for Best Original Score for The Lion King (1994), and for Dune (2021). His works include Gladiator, The Last Samurai, the Pirates of the Caribbean series, The Dark Knight trilogy, Inception, Man of Steel, Interstellar, Dunkirk, No Time to Die, and the Dune series.
Zimmer spent the early part of his career in the United Kingdom before moving to the United States. He is the head of the film music division at DreamWorks Pictures and DreamWorks Animation studios and works with other composers through the company that he founded, Remote Control Productions, formerly known as Media Ventures.
His studio in Santa Monica, California, has an extensive range of computer equipment and keyboards, allowing demo versions of film scores to be created quickly.
Zimmer has collaborated on multiple projects with directors including Christopher Nolan, Ridley Scott, Ron Howard, Gore Verbinski, Michael Bay, Guy Ritchie, and Denis Villeneuve.
Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
His works are notable for integrating electronic music sounds with traditional orchestral arrangements. Since the 1980s, Zimmer has composed music for over 150 films.
He has won two Academy Awards for Best Original Score for The Lion King (1994), and for Dune (2021). His works include Gladiator, The Last Samurai, the Pirates of the Caribbean series, The Dark Knight trilogy, Inception, Man of Steel, Interstellar, Dunkirk, No Time to Die, and the Dune series.
Zimmer spent the early part of his career in the United Kingdom before moving to the United States. He is the head of the film music division at DreamWorks Pictures and DreamWorks Animation studios and works with other composers through the company that he founded, Remote Control Productions, formerly known as Media Ventures.
His studio in Santa Monica, California, has an extensive range of computer equipment and keyboards, allowing demo versions of film scores to be created quickly.
Zimmer has collaborated on multiple projects with directors including Christopher Nolan, Ridley Scott, Ron Howard, Gore Verbinski, Michael Bay, Guy Ritchie, and Denis Villeneuve.
Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
1996dec6:06979880
posted
2 days ago
Exclusive #bitcoin life
Good morning people
Saturday morning
after Friday party night
with songs from
Saturday night fever
#coffe #nostr #plebchain 

733fcc25:471bf3ec
posted
2 days ago
BITCOIN WARNING! 🚨⬇️
The market is taking a hit! Our bot has detected a strong selling opportunity for #Bitcoin.
Sell your #BTC now and lock in those profits while they're hot! 🔥
Signal: SELL
Disclaimer: Our bot's signals are not investment advice. Always do your own research and consult with a financial expert before making any investment decisions.
0f389bba:9b3f148f
posted
2 days ago
🌊 SURF 'N TURF 🏝️
-THE ISLAND LIFE-
https://image.nostr.build/9e2e108e30c6b197c381768ba635cca2c544624c43e3627c82890fb2dfc58306.jpg
Candi Sukuh is a 15th-century Hindu temple located on the western slope of Mount Lawu in Central Java, Indonesia.
https://image.nostr.build/bffadbe4b637cc78e11056e7fd091f840f402a852755661c6dff2c4fcddb4171.jpg
Constructed during the Majapahit Empire, it is believed to date to 1437 AD under the rule of King Brawijaya V or one of his successors, during a period of transition as the influence of Islam began to spread across Java. The temple’s purpose appears to have been associated with fertility rites as suggested by its numerous symbolic carvings and sculptures.
https://image.nostr.build/c0514a28070f9bd8afdad168ded7d4eb49ddcf08eac5bf29a1c84505956d3df4.jpg
The temple has a truncated-pyramid design, which resembles Aztec structures more than the typical Javanese-style temples. It is built from andesite stone and features a main entrance flanked by gate structures, with a central courtyard that houses the pyramid and several smaller structures. The temple is adorned with carvings depicting Hindu deities, mythological scenes, and explicit fertility symbols.
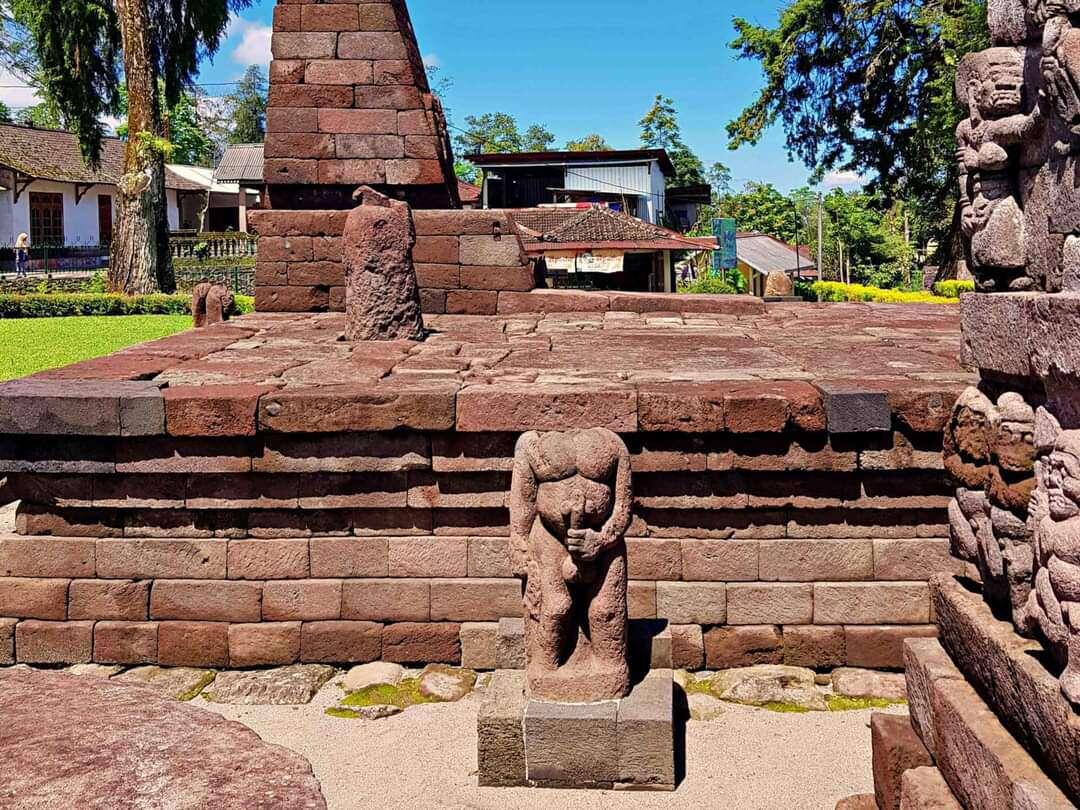 Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
 Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
NunyaBidness
reposted
2 days ago
1408bad0:4971f2ca
posted
2 days ago
Life feels good on a Bitcoin Standard. Knowing each day that your money is a fixed supply. /End Message #bitcoin
0f389bba:9b3f148f
posted
2 days ago
🌊 SURF 'N TURF 🏝️
-THE ISLAND LIFE-
The Underrated Genius of René Descartes
Is the genius of René Descartes is underrated?
Although René Descartes (1596–1650) is often acknowledged for his famous phrases and contributions to Cartesian geometry, the breadth of his influence is frequently underestimated. His work fundamentally shifted how we view knowledge, inquiry, and even the nature of existence. In this sense, he is an underrated genius whose visionary ideas are woven through multiple disciplines—sometimes so deeply embedded that they’re overlooked. He made groundbreaking contributions across multiple fields, including philosophy, mathematics, and science.
Here’s an overview of some of his most influential contributions:
1. Philosophy: Cogito, Ergo Sum (“I Think, Therefore I Am”)
• Descartes’ most famous philosophical assertion, “Cogito, ergo sum,” was a foundational moment in Western thought. In his search for certainty, he arrived at the realization that while he could doubt everything, he could not doubt his own act of doubting, and thus, his existence. This insight established a basis for self-awareness and individual consciousness as fundamental truths.
• His method of methodological skepticism—doubting everything that could not be proven with absolute certainty—helped shape modern approaches to scientific inquiry and knowledge.
2. Dualism: Mind-Body Separation
• Descartes developed the concept of dualism, which posits that mind and body are fundamentally different substances. According to Descartes, the mind (a non-material substance) is separate from the body (a material substance), and they interact through the pineal gland. This idea had a profound influence on philosophy, psychology, and neuroscience, sparking debates that continue today about the nature of consciousness and the relationship between the mental and physical worlds.
3. Analytical Geometry
• In mathematics, Descartes’ analytical geometry revolutionized the field. He introduced a way to describe geometry through algebra by plotting points on a Cartesian coordinate system (named after him). This innovation allowed geometric shapes to be expressed as algebraic equations and enabled the development of calculus by Newton and Leibniz.
• The Cartesian plane (using x and y coordinates) remains fundamental to mathematics and physics, linking algebra and geometry and providing a basis for graphing functions and data.
4. Cartesian Doubt and Rationalism
• Descartes is often considered the father of rationalism, a philosophical view that emphasizes reason as the primary source of knowledge. His systematic doubt and emphasis on deductive reasoning laid the groundwork for the scientific method, influencing Enlightenment thinkers and shaping the development of Western philosophy.
5. Scientific Contributions and Mechanics
• Descartes made strides in optics, explaining the law of refraction (now known as Snell’s law) and advancing theories about light and vision. His work contributed to the early understanding of how light behaves, helping to bridge the gap between physics and philosophy.
• In mechanics, he proposed that the physical world operated according to certain mechanical laws, laying a foundation for classical physics. Though later revised by Newton, Descartes’ ideas were essential to early conceptions of motion and the mechanistic view of nature.
6. Mathematical and Scientific Terminology
• Descartes introduced terms and conventions still in use today. For instance, he used superscript numbers to denote exponents (e.g., x^2 for x squared), which is now standard in algebra.
• He also introduced the use of letters at the end of the alphabet to represent unknowns (e.g., x, y, z) and letters at the beginning to represent constants (a, b, c), conventions that remain essential in algebra.
7. Influence on Medicine and Neuroscience
• Though not entirely accurate by modern standards, Descartes’ ideas on the interaction between mind and body contributed to early studies in neuroscience and psychology. His view that the mind affects the body through the pineal gland was one of the first attempts to explain brain function, stimulating later research into the physiological basis of thought and behavior.
Summary
Descartes’ work in philosophy, mathematics, and science makes him the grandfather of modern thought, emphasizing skepticism, analytical reasoning, and the pursuit of knowledge through rational inquiry. His legacy endures in fields ranging from mathematics and computer science to philosophy and cognitive science, making him a pivotal figure in the development of Western intellectual history.
 Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
 Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
0f389bba:9b3f148f
posted
2 days ago
🌊 SURF 'N TURF 🏝️
-THE ISLAND LIFE-
https://image.nostr.build/6230e41152428f7caceb99eb41e971dd03a9870cd29a4e1ee5cfc24e61cdac5e.jpg
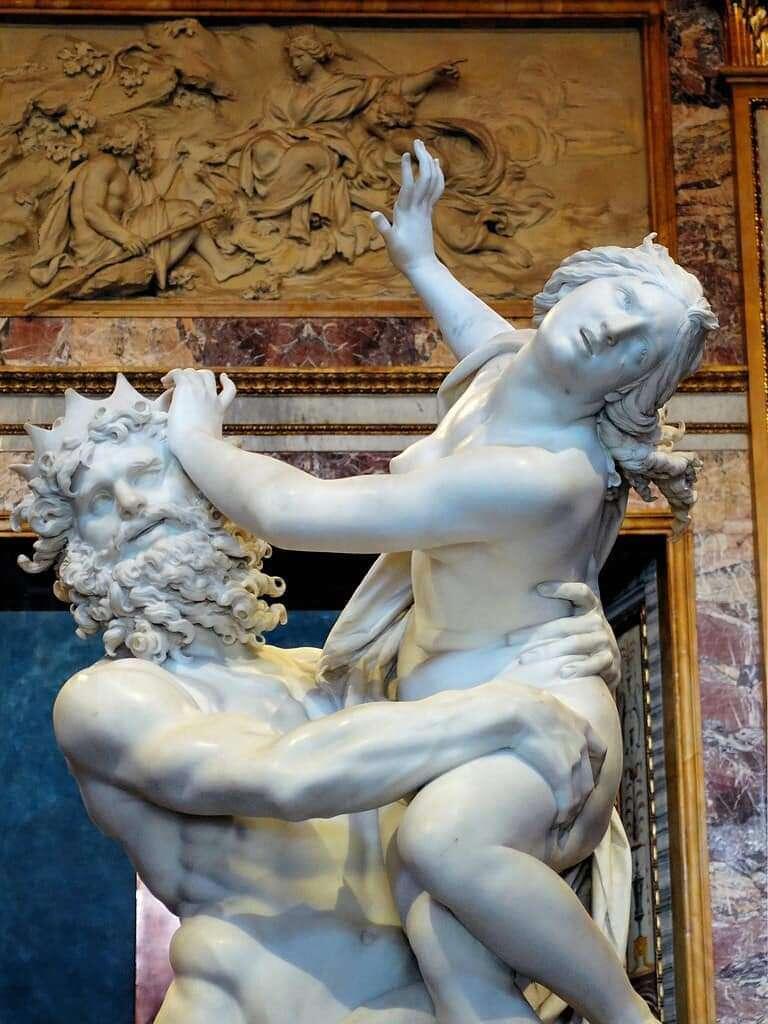
Gian Lorenzo Bernini's famous sculpture "The Abduction of Persephone" (Ratto di Proserpina) with the expression on Persephone’s face and tears, 1622,
Borghese Gallery, Rome, Italy.
https://image.nostr.build/664055e8a3e7789f3b906f4c8078fe809baeab3770759571e097715b6d8413fb.jpg
"A large Baroque marble group sculpture made by Bernini between 1621 and 1622, at an early stage in the artist's career.
https://image.nostr.build/737353c5f8332814784dd3685ded23d9737dc1e77b66c23a54aab7648e3d7018.jpg
Completed when Bernini was only 23, the sculpture depicts the abduction of Persephone who is abducted by the god Pluto and taken to the underworld."
 Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
 Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
Credits Goes to the respective
Author ✍️/ Photographer📸
🐇 🕳️
#Bitcoin #Satoshis #Freedom #Apocalypse #Music #Movies #Philosophy #Literature
stacksatsio
posted
2 days ago
You’d be surprised. These are not impressive people, they are party apparatchiks.
I’m certain there are people inside the central banks who understand it completely and others who at least understand enough that it’s a threat to them, but someone like Bullock whose been inside the RBA for decades or Kroger whose a Liberal Party stooge, they’re not the kind of people who go and expand their minds with novelties.
They exist in a power structure and that’s all they know. Anything outside of that seems irrelevant to them because they don’t imagine there are other avenues of power being the midwits they are.
Cyph3rp9nk
reposted
2 days ago
{"id":"eb9c5adadc2271b3a269043b0800ebbfd40d5214acbe18ac7fbe0d45efbe252f","sig":"a1bf0d8c1c1fa830178703ef9fede57969646adf8e8c4f3b454dbc610b74cf2e085f2a832af69a5eeacdb7f8df56e8a3f12c5bffa11cbef2feb383a0c77227cb","kind":1,"tags":[["imeta","url https://v.nostr.build/QJVjrZ4PtZi1k4eV.mp4","blurhash eJIXs%589]~A4:x].8kWROt7JC$*$*XS%2tmi_%LS%s:Rkt7Rjaeof","dim 720x1280"],["r","https://v.nostr.build/QJVjrZ4PtZi1k4eV.mp4"]],"pubkey":"7ca66d4166b16f54a16868191ba1c6386a976624f4634f3896d9b6740a388ca3","content":"💅 https://v.nostr.build/QJVjrZ4PtZi1k4eV.mp4 ","created_at":1731743051}